🔐 Encrypted Data Transmission (Keepz API)
To ensure the security of your data, all communication with Keepz uses hybrid encryption — combining AES-256-CBC and RSA.
This ensures that:
- Only Keepz can read your requests
- Only you can read Keepz’s responses
When sending API requests to Keepz, these three parameters must always be included — but note that in some requests they will be sent in the body, while in others they may appear as query parameters:
{
"encryptedData": "string",
"encryptedKeys": "string",
"aes": true
}
Parameter details
encryptedData
- Contains the actual request payload.
- The payload is encrypted using a randomly generated symmetric key and IV (Initialization Vector).
- The symmetric key and IV change with each request to ensure security.
encryptedKeys
- Contains the AES key and IV used to encrypt encryptedData.
- TThe AES key and IV are Base64-encoded, concatenated with a dot (.), then encrypted using the RSA public key provided by Keepz during integration.
- Only Keepz (with the matching RSA private key) can decrypt it.
aes
- Boolean flag indicating that the request uses AES-based symmetric encryption (needed for backward compatibility with older encryption methods).
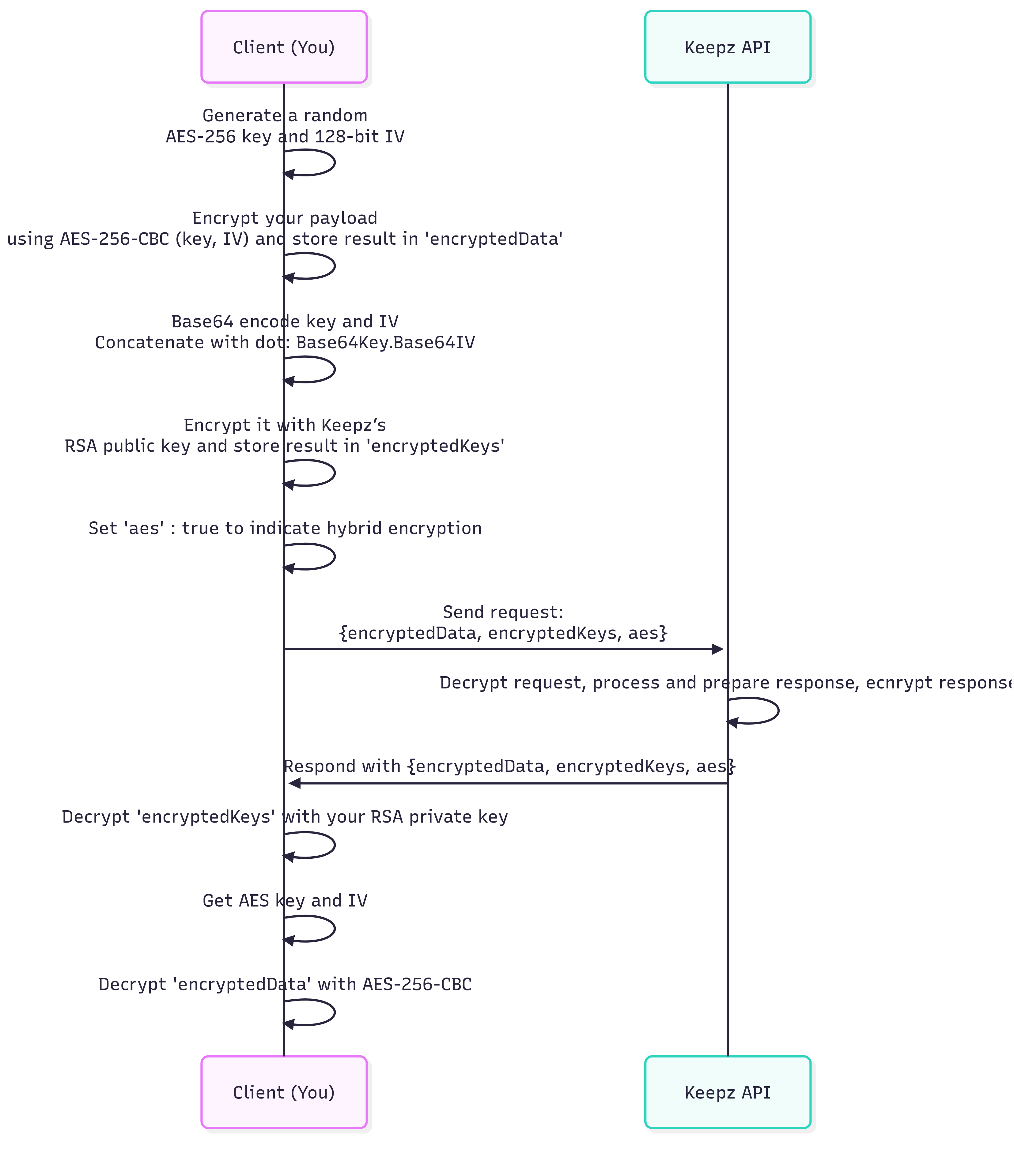
How to Send Encrypted Requests
🔹 1. Encrypt the Payload:
- Use AES-256-CBC to encrypt your original data (like amount, receiverId, etc.).
- Generate:
- A 256-bit AES symmetric key
- A 128-bit IV (Initialization Vector)
- Use this AES key and IV to encrypt your payload, and put the result into encryptedData.
🔹 2. Encrypt the Key & IV
- Base64 encode both the AES key and IV
- Concatenate them with a dot: Base64Key.Base64IV
- Encrypt this string with Keepz’s RSA public key
- Base64 the encrypted result and put result into encryptedKeys
🔹 3. Set aes: true
This tells our system you’re using AES-based encryption.
⸻
📨 What Happens on Our Side
- We decrypt encryptedKeys using our private RSA key
- Split the result to get the AES key and IV
- Use them to decrypt encryptedData
⸻
🔁 Decrypting Our Responses
We respond using the same method:
{
"encryptedData": "string",
"encryptedKeys": "string",
"aes": true
}
- Use your RSA private key to decrypt encryptedKeys
- Decode the symmetric key and IV
- Use them to decrypt the response data inside encryptedData
🔒 Why This is Secure
- AES key is never exposed
- RSA encryption ensures only the intended party can access the AES key
- IV makes output unique every time, even with same input
- Full encryption at every step
{
"encryptedData": "U2FsdGVkX1+...==",
"encryptedKeys": "TGl2ZUtleS5JVg==",
"aes": true
}
Padding mode
⚠️ Keepz encryption supports RSA padding mode:
- RSA/ECB/OAEPWithSHA-256AndMGF1Padding
🔧 Code Implementation Examples
Here are example snippets showing how to implement the encryption and decryption process for Keepz requests and responses.
Schema
This diagram illustrates the encryption flow between the integrator and Keepz, showing how data is encrypted with a symmetric key (AES), the key is encrypted with the integrator's public RSA key, and both are transmitted securely.